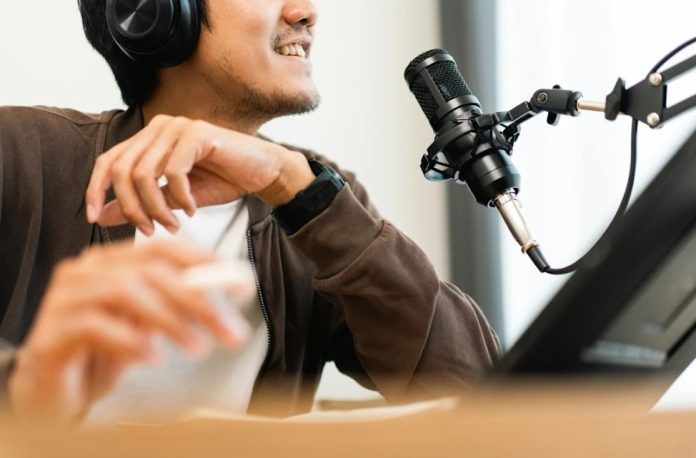
In the vast world of audio technology, microphones stand as unsung heroes, transforming sound waves into electrical signals. Whether you’re an aspiring musician, a podcaster, or simply intrigued by the mechanics of sound capture, understanding how microphones work is key to harnessing their potential.
Microphones, commonly known as mics, are devices that convert acoustic energy (sound) into electrical signals. These signals can then be amplified, recorded, or transmitted for various purposes.
Delving into the intricacies of microphone functionality allows users to make informed choices, optimize performance, and troubleshoot issues effectively.
Explore the detailed comparison between Shure MV7 and SM7B to make an informed decision about your next microphone upgrade: Shure MV7 vs SM7B models.
Types of Microphones
Microphones come in various types, each with its unique design and functionality, catering to different recording scenarios and preferences. Understanding the intricacies of these microphone types can significantly impact the quality of audio capture in specific situations.
Dynamic Microphones
Dynamic microphones are renowned for their robust build and versatility. Operating on the principle of electromagnetic induction, these mics boast a diaphragm attached to a coil within a magnetic field. When sound waves hit the diaphragm, it moves the coil, generating an electrical current. Dynamic microphones are ideal for high-volume environments, making them a preferred choice for live performances and recording loud instruments due to their ability to handle loud sound sources with minimal distortion.
Condenser Microphones
Condenser microphones, in contrast, utilize a diaphragm placed close to a backplate, forming a capacitor. Sound waves cause variations in the distance between the diaphragm and backplate, resulting in electrical changes. Known for their sensitivity and ability to capture a broad frequency range, condenser microphones are commonly used in studio settings for vocals and nuanced sound sources. They excel in delivering detailed and high-quality audio recordings.
Ribbon Microphones
Ribbon microphones employ a thin strip of metal (the ribbon) suspended in a magnetic field. When sound waves move the ribbon, it generates an electrical current. Recognized for their warm and natural sound reproduction, ribbon microphones are often chosen for capturing the subtle nuances in audio. While they may require careful handling due to their delicate nature, their unique sonic characteristics make them valuable in specific recording applications.
Microphone Components
To comprehend the intricate workings of microphones, it’s essential to explore the fundamental components that collaborate to transform sound waves into electrical signals.
- Diaphragm. The diaphragm serves as the microphone’s sensory organ, a thin and responsive material that vibrates in response to incoming sound waves. Its ability to move in sync with these vibrations is critical for initiating the signal conversion process.
- Coil or Capacitor. In both dynamic and condenser microphones, the coil or capacitor plays a pivotal role in converting mechanical vibrations into electrical signals. In dynamic microphones, the movement of the coil within a magnetic field generates an electrical current, while in condenser microphones, variations in the capacitor’s electrical charge occur.
- Magnet. The magnet is a key component that creates a magnetic field. This field interacts with the coil or capacitor, facilitating the generation of an electrical current. The strength and configuration of the magnet influence the microphone’s overall performance.
- Housing. While often overlooked, the housing of a microphone is crucial. It protects the delicate internal components from external elements and influences the microphone’s durability, design, and overall aesthetic. The housing can impact the microphone’s ability to reject unwanted noise and contribute to its overall sound signature.
Polar Patterns
In the realm of microphones, polar patterns play a pivotal role in defining how a microphone captures sound from different directions. Understanding these patterns is crucial for achieving optimal audio results in various recording scenarios.
- Omnidirectional. Omnidirectional microphones exhibit a 360-degree sensitivity, capturing sound equally from all directions. While versatile, these microphones are susceptible to picking up background noise, making them ideal for controlled environments where ambient sounds are minimal.
- Cardioid. Cardioid microphones focus on capturing sound primarily from the front, forming a heart-shaped sensitivity pattern. This design minimizes noise from the sides and rear, making cardioid microphones ideal for isolating a specific sound source in a noisy environment.
- Bidirectional. Bidirectional, or figure-eight, microphones are sensitive to sound from the front and rear while rejecting sound from the sides. This pattern is beneficial for scenarios like interviews where the microphone can capture two opposite-facing sources simultaneously.
- Hypercardioid. Hypercardioid microphones have a more concentrated front sensitivity compared to cardioid patterns, further minimizing side and rear sound pickup. This makes them suitable for environments where isolating a specific sound source is crucial, such as on-stage performances.
Connection Types
Microphones offer various connection options, impacting both compatibility and functionality. USB microphones, designed for simplicity, serve as plug-and-play devices, catering to beginners and individuals focused on computer-based recording. On the other hand, XLR microphones deliver a caliber of audio quality suitable for professional applications, finding common usage in both studio settings and live performances. The choice between USB and XLR connections depends on the user’s specific needs, with USB providing convenience and accessibility, while XLR ensures a higher standard of audio performance, meeting the demands of more advanced recording environments.
Microphone Placement
Careful placement of microphones is essential to attain superior sound quality and diminish undesirable noise. Experimenting with positioning to discover the optimal “sweet spot,” taking room acoustics into account, and incorporating pop filters to mitigate plosive sounds are strategic approaches. Achieving the perfect microphone placement involves a thoughtful consideration of the recording environment, utilizing experimentation and acoustic adjustments. These practices contribute to the creation of clear and high-quality audio recordings while effectively managing potential challenges associated with ambient noise and vocal nuances.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting
Addressing background noise involves optimizing recording environments, using noise reduction tools, and selecting the right microphone type.
Distortion issues may arise from excessive input levels; adjusting gain settings and maintaining appropriate distances can help mitigate distortion.
Low volume problems might be solved by checking cable connections, adjusting input levels, and ensuring proper microphone sensitivity.
Maintenance Tips
Consistent microphone maintenance is imperative for sustained optimal performance. Routinely cleansing the microphone, paying particular attention to the delicate diaphragm, is crucial to ward off dust buildup that could compromise functionality. To safeguard the microphone from potential harm and extend its lifespan, secure storage in a protective case or pouch is recommended. This practice not only shields the device from external elements but also minimizes the risk of damage, ensuring that the microphone remains in peak condition for an extended duration. Incorporating these maintenance steps becomes a proactive measure in preserving the microphone’s functionality and durability.
Applications of Microphones
Microphones hold pivotal significance across diverse domains, each demanding specific functionalities. Within the studio environment, these devices meticulously capture the intricacies of musical performances, enhancing the creation of top-tier recordings. Podcasters heavily depend on microphones to articulate their voices with precision, fostering a more intimate connection with their audience. In expansive venues, microphones serve as amplifiers, guaranteeing that the voices of performers resonate effectively and reach the farthest corners of the audience, ensuring an immersive and impactful experience for all attendees. The unique applications of microphones underscore their versatility and indispensability across various facets of communication and entertainment.
Benefits of Understanding Microphone Functionality
Gaining a profound insight into the workings of microphones grants users the capability to fine-tune settings, resulting in unparalleled audio quality. Mastery over the intricacies of these devices elevates the overall user experience, be it in content creation or live engagements. This enhanced comprehension enables users to make informed decisions, ensuring optimal performance tailored to specific requirements. Whether crafting content in a studio or engaging with live audiences, the knowledge of microphone functionality becomes a cornerstone for achieving superior audio outcomes, fostering a more enriched and satisfying experience for both creators and listeners alike.
Conclusion
In the realm of audio technology, the magic of microphones unfolds as they seamlessly convert sound into electrical signals. Armed with the knowledge of microphone types, components, and applications, users can navigate the diverse landscape of sound capture with confidence.